Introduction
The Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) algorithm is a set of clinical guidelines and protocols designed to manage life-threatening cardiovascular emergencies, including cardiac arrest, stroke, and acute coronary syndromes. Developed by the American Heart Association (AHA), ACLS provides a structured approach for healthcare professionals to improve patient outcomes during critical situations.
This article explores the key components of the ACLS algorithm, its steps, and its importance in emergency medical care.
What is the ACLS Algorithm?
The ACLS algorithm is a step-by-step decision-making tool that guides medical professionals in treating cardiovascular emergencies. It integrates:
-
Basic Life Support (BLS) fundamentals (e.g., high-quality CPR).
-
Pharmacological interventions (e.g., epinephrine, amiodarone).
-
Electrical therapies (e.g., defibrillation, pacing).
-
Team dynamics for efficient resuscitation.
The algorithm is updated periodically based on the latest evidence-based research to ensure optimal patient care.
Key Components of the ACLS Algorithm
The ACLS algorithm consists of several critical pathways, including:
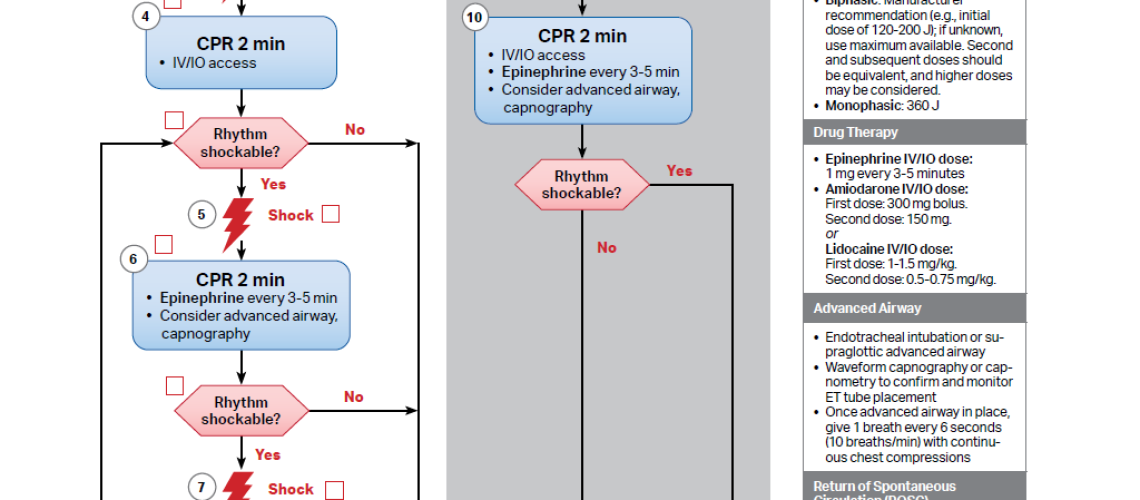
1. Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
The most widely recognized ACLS algorithm focuses on pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF), pulseless electrical activity (PEA), and asystole. The steps include:
-
Immediate CPR (30 compressions to 2 breaths).
-
Early defibrillation (for shockable rhythms: VF/pulseless VT).
-
Administration of medications (e.g., epinephrine, amiodarone).
-
Post-resuscitation care (e.g., targeted temperature management).
2. Bradycardia & Tachycardia Algorithms
-
Bradycardia: If a patient has a slow heart rate (<50 bpm) with symptoms (e.g., hypotension, syncope), interventions include atropine, transcutaneous pacing, or dopamine/epinephrine infusion.
-
Tachycardia: For unstable patients with rapid heart rates (>150 bpm), synchronized cardioversion may be needed. Stable patients may receive medications like adenosine (for SVT) or antiarrhythmics (e.g., amiodarone for VT).
3. Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) & Stroke Algorithms
-
ACS: Focuses on rapid recognition, aspirin administration, nitroglycerin, and reperfusion strategies (e.g., PCI or fibrinolytics).
-
Stroke: Emphasizes the FAST assessment (Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, Time to call 911) and rapid transport to a stroke center for thrombolytics or thrombectomy.
Why is the ACLS Algorithm Important?
-
Standardized Approach: Ensures consistency in emergency care.
-
Improves Survival Rates: Early defibrillation and high-quality CPR increase survival in cardiac arrest.
-
Reduces Errors: Structured decision-making minimizes mistakes during high-stress situations.
-
Enhances Team Coordination: Clear roles and communication improve resuscitation efforts.
Conclusion
The ACLS algorithm is a vital tool in emergency medicine, providing a systematic approach to managing cardiovascular crises. By following evidence-based protocols, healthcare providers can optimize patient outcomes and save lives. Regular training and certification in ACLS ensure that medical professionals remain proficient in these life-saving techniques.
For those in healthcare, mastering the ACLS algorithm is not just a requirement—it’s a commitment to delivering the highest standard of care in critical moments.
Visit our website: